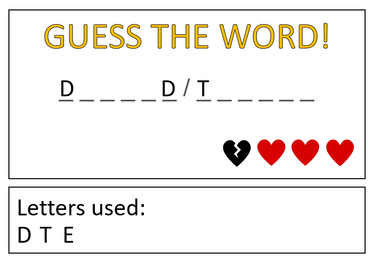
Guess the word (Python)
Guess the word tutorial
Learning Objectives:
- Understand and use sequence in an algorithm
- Understand and use iteration in an algorithm (FOR and WHILE loops)
- Understand and use selection in an algorithm (IF, Else and Else if)
- Understand why it is so difficult to create a computer that can seemingly think for itself
- Understand and use data structures in an algorithm (for example, Lists, Tables or Arrays)
Curriculum Mapping:
KS2:
- Design, write and debug programs that accomplish specific goals; solve problems by breaking them into smaller parts. Select, use and combine a variety of software on a range of digital devices to design and create a range of programs.
- Use sequence, selection and repetition in programs; work with variables and various forms of input and output
- Use logical reasoning to explain how some simple algorithms work; detect and correct errors in algorithms and programs
KS3:
- Use two or more programming languages, at least one of which is textual, to solve a variety of computational problems.
STUDENT: COMPUTATIONAL THINKER:
- 5a: Students break problems into component parts, extract key information, and develop descriptive models to understand complex systems or facilitate problem-solving.
- 5c: Students break problems into component parts, extract key information, and develop descriptive models to understand complex systems or facilitate problem-solving.
- 5d: Students understand how automation works and use algorithmic thinking to develop a sequence of steps to create and test automated solutions.
EDUCATOR: COMPUTATIONAL THINKING COMPETENCIES:
- 4b: Design authentic learning activities that ask students to leverage a design process to solve problems with awareness of technical and human constraints and defend their design choices.
COMPUTER SCIENCE EDUCATORS:
- 2a: Plan and teach computer science lessons/units using effective and engaging practices and methodologies:
i. Select a variety of real-world computing problems and project-based methodologies that support active and authentic learning and provide opportunities for creative and innovative thinking and problem solving
ii. Demonstrate the use of a variety of collaborative groupings in lesson plans/units and assessments
iii. Design activities that require students to effectively describe computing artifacts and communicate results using multiple forms of media
iv. Develop lessons and methods that engage and empower learners from diverse cultural and linguistic backgrounds
v. Identify problematic concepts and constructs in computer science and appropriate strategies to address them
vi. Design and implement developmentally appropriate learning opportunities supporting the diverse needs of all learners
vii. Create and implement multiple forms of assessment and use resulting data to capture student learning, provide remediation and shape classroom instruction
CSTA K–12 CS Standards:
- 1B-AP-08: Compare and refine multiple algorithms for the same task and determine which is the most appropriate.
- 1B-AP-09: Create programs that use variables to store and modify data.
- 1B-AP-10: Create programs that include sequences, events, loops, and conditionals.
- 1B-AP-11: Decompose (break down) problems into smaller, manageable subproblems to facilitate the program development process.
- 1B-AP-13: Use an iterative process to plan the development of a program by including others' perspectives and considering user preferences.
- 1B-AP-15: Test and debug (identify and fix errors) a program or algorithm to ensure it runs as intended.
- 1B-AP-17: Describe choices made during program development using code comments, presentations, and demonstrations.
- 2-AP-11: Create clearly named variables that represent different data types and perform operations on their values
- 2-AP-12: Design and iteratively develop programs that combine control structures, including nested loops and compound conditionals.
- 2-AP-15: Seek and incorporate feedback from team members and users to refine a solution that meets user needs.
- 2-AP-16: Incorporate existing code, media, and libraries into original programs, and give attribution.
- 2-AP-17: Systematically test and refine programs using a range of test cases.
- 3A-AP-14: Use lists to simplify solutions, generalizing computational problems instead of repeatedly using simple variables.
- 3A-AP-15: Justify the selection of specific control structures when tradeoffs involve implementation, readability, and program performance, and explain the benefits and drawbacks of choices made.
AREA OF LEARNING AND EXPERIENCE: Science and Technology:
Computation is the foundation for our digital world.
Progression step 3
- I can use conditional statements to add control and decision-making to algorithms.
- I can identify repeating patterns and use loops to make my algorithms more concise.
- I can explain and debug algorithms.
Progression step 4
- I can decompose given problems and select appropriate constructs to express solutions in a variety of environments.
- I can select and use data structures that efficiently manage data in algorithms.
- I can plan and implement test strategies to identify errors in programs.
Progression step 5
- I can identify, define and decompose problems, choose appropriate constructs and express solutions in a variety of environments.
- I can use file-handling techniques to manipulate data in algorithms.
- I can test, evaluate and improve a solution in software.
How the game works
1. The game will start by picking a random word or phrase from a list.
2. Next, each letter in the word or phrase is replaced by a dash '-' or 'underscore '_'.
e.g.
DONALD TRUMPS
becomes
_ _ _ _ _ _ / _ _ _ _ _ _
3. Finally, the player must guess the word by suggesting different letters.
Rules:
- If the player guesses a correct letter, the letter is revealed in the phrase.
- For each letter the player guesses wrong, the player will lose a life.
Before creating their 'guess the word game', start by having the students explore some of the functions they will be using.
STEP 1
Start by sharing the following line of code to replace a character at specific index in a string.
Explain to the students that to replace a character with a given character at a specified index, you can use python string slicing as shown below:
|
string = "pythonhxamples"
position = 6 character = "e" string = string[:position] + character + string[position+1:] print(string) |
Explain that, in our game, we need to replace each letter in our word or phrase with a dash '-' or 'underscore '_'.
Challenge 1
- Challenge the students to modify their code (above) so that it changes the 3rd letter to an underscore '_'.
Explain to the students that in order to change all the letters in our word or phrase, they are going to need a loop.
Ask the students copy and run the following code (You can try the code yourself using the code window above):
|
string = "TRUMP"
character = "_" for i in range (len(string)): string = string[:i] + character + string[i+1:] print(string) |
Explain to the students that because there are no spaces in between each of the hidden letters, we can't tell how many letters there are in our word!
Ask the students to replace the last line in their code with the following.
Important! (Inform students that they must ensure that they put a space between the two speech marks " "):
|
print(" ".join(string))
|
Explain to the students that in order to make our game more challenging, each time the player plays the game it will pick a new word at random from a list.
Start by having the students practice this by creating a random name picker.
STEP 1
Tell the students that they are now going to create a random name picker and that this will form the basis of their 'guess the word' game.
Share the following code for students to copy (You can test this for yourself using the code window below):
|
import random
names = ["Bob", "Dave", "Stuart"] print(names[random.randint(0,2)]) |
Ask the students to comment their code, using the hashtag (#), to explain what each line of the code is doing and why the random generator is returning a value between 0 and 2 rather than 1 and 3.
Explain to the students that lists start at 0 NOT 1.
e.g. if we were to run the following code:
print(names[0])
The computer would return the name “Bob”
STEP 2
- Ask the students to replace the last line with the following new code:
|
print(random.choice(names))
|
Have the students run their new script and explain what the new code does.
STEP 3
Finally, explain to the students that, in order for our program to work, we need to add (concatenate) the word “Minion” at the beginning of our randomly selected name.
- Ask the students to replace the last line with the following:
|
print(“Minion” + “ “ + random.choice(names))
|
Challenge:
- Ask the students to add some more names to their list.
Explain to the students that they now have all the components they need to create their very own guess the word game.
Share the following code for students to copy (You can try the code yourself using the code window below):
|
import random
#create a list of hangman words wordList = ["cat","dog","mouse"] #choose a word from the list at random wordChosen = random.choice(wordList) #create an empty list to store the used letters used = [] #create a variable to store and display the player's guesses display = wordChosen for i in range (len(display)): #replace each letter with a '_' display = display[0:i] + "_" + display[i+1:] #put a space between each dash print (" ".join(display)) #counter stops the game once all letters have been guessed correctly attempts = 0 #keep asking the player untill all letters are guessed while display != wordChosen: guess = input("Please enter a letter: ") guess = guess.lower() #Add the players guess to the list of used letters used.extend(guess) print ("Attempts: ") print (attempts) #Search through the letters in answer for i in range(len(wordChosen)): if wordChosen[i] == guess: display = display[0:i] + guess + display[i+1:] print("Used letters: ") print(used) #Print the string with guessed letters (with spaces in between)) print(" ".join(display)) attempts = attempts + 1 print("Well done, you guessed right!) |
| guess_the_word_solution.zip |
Challenge the students to...
- Modify their code so that it tells the player how many guesses they made.
- Add some more words or phrases to their list.
- Modify their code so that it replaces spaces (" ") in a phrase with a slash "/".
- Add a 'life counter' and remove a life every time a player guesses an incorrect letter. The game ends if the player guesses correctly or they run out of lives (which ever comes first).
Unless otherwise specified, everything in this repository is covered by the following licence: